Introduction
Thrombocytopenia, which signifies a low platelet count usually below 150 × 109/L, a number of causes lead to thrombocytopenia, like drug induced, heparin induced, neonatal factors, gestational, chemothepeutic and viral, Drug induced thrombocytopenia is clinical disorder, caused due to administration of therapeutic drugs for management of various diseases. More than 300 drugs are identified that can cause drug induced thrombocytopenia,1 the symptoms may begin in 5 to 10 days of drug administration, even with single dose administration can cause immediate effects, the stopping of drugs for 1 to 2 days can recover the patients from complication related to drug effects, the common drugs that lead to drug induced thrombocytopenia are quinidine, vancomycin oxaliiplatin, suramin, abciximab, tirofiban, heparin, pencillin, sulfonamide, statins, ranitidine, NSAIDs’.
Heparin is the drug used for thromboprophylaxis in cardiovascular diseases, neuro disorders, dialysis, extracorporeal circulation, but the drug has adverse effect and patients are at risk of developing, heparin induced thrombocytopenia, 2, 3 Heparin induced thrombocytopenia is clinical disorder, caused due to immune mediated adverse reaction resulted from emergence of antibodies which activated micro particles of platelets in presence of heparin.
Platelets are formed in blood by 5 weeks sooner than within 30 weeks the platelets are fully functional and help in repair and reformulation of neonate structures, due to immune mediate, alloimmune and maternal antibodies the decrease in platelets occur within 72 hours of birth, this thrombocytopenia can be mild, moderate and severe, if the onset is later 72 hours can cause intraventricular hemorrhage. The mild and moderate neonatal thrombocytopenia resolves within 10days. If severe case needs better investigation and management. 4, 5
Gestational thrombocytopenia is condition with platelets count less than 50000 in a pregnant women, the incidence is asymptomatic and occurs in second half of pregnancy, 6, 7 in the absence of history of thrombocytopenia the of platelets count returns to normal level within two months of postpartum.8 The gestational thrombocytopenia is not associated with maternal or fetal risk.9 Even after less risk for mother and child the gestational thrombocytopenia can be serious issue and can cause potential problems 10 to mother during labor and postpartum period,
Thrombocytopenia, an abnormally low blood platelet count, is a common side effect of myelosuppressive chemotherapy. 11, 12, 13 Prior studies estimated that approximately 10% to 38% of patients with a solid tumor and 40% to 68% of patients with a hematologic malignancy experience thrombocytopenia.14, 15, 16, 17 The incidence and prevalence of chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia vary greatly by type of cancer and chemotherapy regimen, for example, from 16% in head and neck cancer to 68% in hematologic cancers, and from 8% in taxane based regimens to 37% in gemcitabine based regimens and 82% in carboplatin monotherapy.12, 13, 17, 18 Gemcitabine based and platinum based regimens have consistently been associated with the highest risk of thrombocytopenia. 11, 12, 14 In solid tumor patients, the highest prevalence of thrombocytopenia was observed in patients with colorectal cancer, followed by non-small cell lung cancer, and ovarian cancer. 13 Currently, there are no standardized guidelines for the prevention or treatment of chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia. To reduce the risk of bleeding or need for transfusions among patients with severe chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia, chemotherapy dose is typically modified, which may decrease relative dose intensity and reduce treatment efficacy.
Viral infection induced thrombocytopenia is a common finding following or during many viral infections. Mild thrombocytopenia, combined with lymphopenia in a patient with signs and symptoms of an infectious disease, raises the suspicion of a viral infection. This phenomenon is classically attributed to platelet consumption due to inflammation-induced coagulation, sequestration from the circulation by phagocytosis and hypersplenism, and impaired platelet production due to defective megakaryopoiesis or cytokine-induced myelosuppression. Platelets as passive bystanders during viral infection. Platelets are increasingly recognized as active players in the (antiviral) immune response and have been shown to interact with cells of the innate and adaptive immune system as well as directly with viruses. 19
The present study assesses the various causes and prevalence of these factor in thrombocytopenia in selected cites of North India.
Objectives
The present study aimed to assess the prevalence of prevalence of thrombocytopenia in Indian patients.
Materials and Methods
A survey study designed to assess the prevalence of thrombocytopenia among patients in multiple cities at north India the cities selected are Lakhimpur, Panipat, Sonipat, Gohana, Delhi for a period of 11 months from January 2022 to November 2022. A total of 22832 patients samples from 5 cities were selected from different diagnostic centers, of these 1295 blood samples showed the prevalence of thrombocytopenia, of which 5440 samples of which 261 showed thrombocytopenia caused due to drug used for treatment, 2860 samples studied 109 showed thrombocytopenia due to heparin, 3250 samples of which 112 showed thrombocytopenia due to neonatal complication, 3952 samples of which 137 showed thrombocytopenia due gestational, 1745 samples of which 281 showed thrombocytopenia due to chemo-drugs use, 5585 samples of which 395 showed thrombocytopenia due to viral infection.
Results
The present study designed to assess the prevalence of thrombocytopenia among Indian patients. The following are the findings of the study identifying various causes for thrombocytopenia among Indian
Table 1
Describes the distribution of the prevalence of thrombocytopenia among Indian patients at various cities under study.
The data is graphically represented in column bar diagram showing the total number of samples collected and number of positive thrombocytopenia samples identified due to various causes among Indian patients under study.(Table 1)
The prevalence rate of various causes are as follows,
The prevalence of g induced drug thrombocytopenia
Table 2
Describes the distribution of the drug induced thrombocytopenia cases at various cities under study.
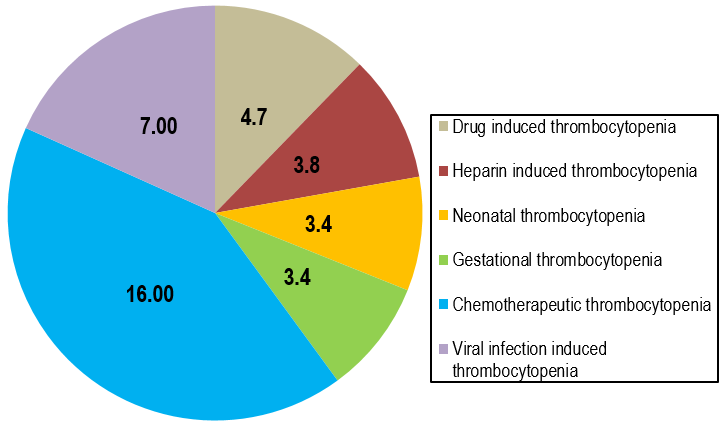
The study found that prevalence of drug-induced thrombocytopenia in total samples of 5440, at Lakhimpur is 3.7%, Panipat is 4.5%, Sonipat is 7.7%, Gohana is 4.7%, Delhi is 4.1% respectively and total prevalence of drug-induced thrombocytopenia in North India is 4.7%.(Table 2)
The prevalence of heparin induced thrombocytopenia
Table 3
Describes the distribution of the heparin-induced thrombocytopenia cases at various cities under study.
The study found that prevalence of heparin induced thrombocytopenia in total samples of 2860, at Lakhimpur is 2.9%, Panipat is 3.5%, Sonipat is 4.4%, Gohana is 4.6%, Delhi is 3.8% respectively and total prevalence of heparin induced thrombocytopenia is 3.8%.(Table 3)
The prevalence of neonatal thrombocytopenia
Table 4
Describes the distribution of the neonatal thrombocytopenia cases at various cities under study.
|
S.No |
City |
Number of samples |
Number of neonatal thrombocytopenia |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Lakhimpur |
545 |
20 |
3.6 |
|
2 |
Panipat |
778 |
31 |
3.9 |
|
3 |
Sonipat |
865 |
32 |
3.6 |
|
4 |
Gohana |
497 |
13 |
2.6 |
|
5 |
Delhi |
565 |
16 |
2.8 |
|
Total |
3250 |
112 |
3.4 |
|
The study found that prevalence of neonatal thrombocytopenia in total samples of 3250, at Lakhimpur is 3.6%, Panipat is 3.9%, Sonipat is 3.6%, Gohana is 2.6%, Delhi is 2.8% respectively and total prevalence of gestational thrombocytopenia is 3.4%.(Table 4)
The prevalence of gestational thrombocytopenia
Table 5
Describes the distribution of the gestational thrombocytopenia cases at various cities under study.
The study found that prevalence of gestational thrombocytopenia in total samples of 3952, at Lakhimpur is 4.3%, Panipat is 3.9%, India is 3.7%, Gohana is 2.5%, Delhi is 2.4% respectively and total prevalence of gestational thrombocytopenia represented is 3.4%.(Table 5)
The prevalence of chemotherapeutic drug induced thrombocytopenia
Table 6
Describes the distribution of the prevalence of thrombocytopenia among patients who were on chemotherapeutic drug at various cities under study.
The study found that prevalence of thrombocytopenia among patients who were on chemotherapeutic drug at various cities for total sample of 1745, at Lakhimpur 13.80%, Panipat 21.28%, Sonipat 17.70%, Gohana 10.99%, Delhi 15.28% respectively and total prevalence of thrombocytopenia among patients who were on chemotherapeutic drug at various cities under study in North India is 16.01%.(Table 6)
The prevalence of viral infection induced thrombocytopenia
Table 7
Describes the distribution of the prevalence of thrombocytopenia among patients with viral infection at various cities under study.
The study found that prevalence of thrombocytopenia among patients with viral infection at various cities for total sample of 5585, at Lakhimpur 5.00%, Panipat 8.77%, Sonipat 6.26%, Gohana 6.46%, Delhi 8.15% respectively and total prevalence of thrombocytopenia among patients with viral infection at various cities under study in North India is 7.07%.(Table 7)
The overall prevalence of causes of thrombocytopenia is represented in pie diagram.(Figure 1)
Discussion
The present study aimed to study the prevalence of the thrombocytopenia among Indian patients in selected various cities at North India. The study was conducted at 5 cities are Lakhimpur, Panipat, Sonipat, Gohana and Delhi for a period of 11 month from January 2022 to November 2022 collected 22832 samples of which 1295 samples were identified with thrombocytopenia.
The present study designed showed that prevalence of the drug induced thrombocytopenia found that the prevalence is 4.7% in selected cities, these findings were similar to the study.20, 21, 22, 23
The present study designed identified that prevalence of the heparin induced thrombocytopenia found that the prevalence is 3.8% in India these findings were similar to the study.2, 3, 24, 25, 26
The present study designed found that prevalence of the neonatal thrombocytopenia is 3.4% these findings were similar to the study.4, 5, 27
The present study found that the prevalence of gestational thrombocytopenia is 3.4%, these findings were similar to the study.7, 8, 9, 10
The present study designed to assess the prevalence of the thrombocytopenia patients who were on chemotherapy drug found that the prevalence is 16.01% in selected cities, these findings were similar to the study 4% of patients with solid tumors and 16% with hematologic malignancies experienced grade 3 thrombocytopenia.28, 29
The present study designed to assess the prevalence of the thrombocytopenia among patients with viral infection found that the prevalence is 7.07% in selected cities, these findings were similar to the study 17.1% of HIV infected patients developed thrombocytopenia.30
The present study designed to assess the prevalence of the thrombocytopenia among Indian patients by studying various cities and found that the prevalence is 5.6% these findings were unique and the study identified the prevalence in North India.
Conclusion
Thrombocytopenia in short is the decreased platelets in circulating blood, the reasons for decreased thrombocytes are wide and range, the knowledge of occurrence of any cause helps in better management of patient. To which the prevalence will guide the incidence rate so that the right intervention can be practiced to prevent the complication of treatment in case of therapeutic drug or chemo drug use, the other vital events such as gestation and its relating complication helps in better care of maternal health and child, the right incidence of neonatal thrombocytopenia helps in restoring the newborn vitals and life, early and right antibiotic or antiviral drugs can prevent complication due to viral infection, the present study designed to understand the nature of prevalence of thrombocytopenia in selected cities of North India, and found that the prevalence information is important information to prevent, treat and manage thrombocytopenia. The recommend that similar prevalence should be studied in other region for early diagnosis and treatment thrombocytopenia.