Introduction
Presbyopia is an age-related condition where near point of eye recedes beyond the ordinary reading or working distance. In emmetropes it usually starts at around 40 years of age. Common treatments of presbyopia consist of use of reading glasses or bifocal/ multifocal eye glasses. Corrective contact lenses may also be used for correcting presbyopia. Surgical options are also available for correcting presbyopia, including eye surgery. Refractive surgery generally involves reshaping of cornea. Refractive surgery to one eye for near vision while leaving the other eye for distant vision, is one of the modalities that may be employed. Intraocular lens implantation is another surgical option. However, eye glasses may be cosmetically unacceptable, lenses may be cumbersome or provide inadequate treatment, and surgery may be risky. In recent times there has been interest among researchers to develop pharmacological agents to treat presbyopia.1 Karanfil FC et al (2017) 2 in their review article discussed the name, content and mechanism of action of these eye drops. Till date about fourteen commercial and non-commercial drops were used or tried in the treatment of presbyopia. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 Although the success to this aim is not overwhelming, some pharmacological agents have already been approved by U.S. Food and Drug administration.20 However, some other drug which has potential for use in the treatment for presbyopia has not been evaluated till date. One such drug is Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop which is commonly used as an intraocular pressure lowering agent in glaucoma for decades. Long-term evaluation of this drop was investigated in a study for a mean follow-up of 31.6 months in a group of 155 patients (275 eyes) with glaucoma or ocular hypertension, and found to be quite safe, serious side-effect requiring discontinuation was only 1.9%. 21 In a resting state, the tone of the ciliary muscle is maintained by mutually opposite interaction between parasympathetic innervation through M3 receptor and sympathetic innervation through beta 2 adrenoceptor receptors. The parasympathetic innervation tends to contract the ciliary muscle and sympathetic innervation tends to relax the ciliary muscle. Therefore, blocking the sympathetic innervation by instilling beta blocker drug like Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop will increase the tonic accommodation22 (as accommodation is caused by contraction of ciliary muscle) and therefore may be helpful in treatment of presbyopia. This mechanism spares pupillary muscles thus do not have any effect on pupillary diameter and also avoids side- effects of multi- drug combination drops which are currently under investigation. Correction of presbyopia by this mechanism of action of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop was evaluated for the first time in literature by our present study.
Hypotheses on Expected Outcome: Reduction of Near Point of Accommodation and increase of Amplitude of Accommodation are the two desirable outcomes of the study, which would be achieved by increase in tonic accommodation by unique mechanism of action of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop as described above. We also hypothesized that the undesirable side effects that accompany Pilocarpine eye drop, like reduction of distant acuity and reduction of intraocular pressure, would not apply to Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop in our study. This is because of the fact that relieved of relaxing effect on it, excursion of ciliary muscle will be more, covering entire range of accommodation required for distant to near back and forth, thus bringing entire accommodation under facultative control of the individual. Our study would employ once-only one-drop Timolol maleate 0.5%, therefore reduction of intraocular pressure is unlikely to occur in this short term use.
Materials and Methods
Inclusion criteria
Informed consent by the participants.
Emmetropic subjects between 35-45 years age group with distant visual acuity 6/6 with no systemic or ocular pathology.
Intraocular pressure (IOP) 12 - 21 mm of Hg.
The patients included in the study did not receive any chronic mydriatic/miotic therapy previously.
Exclusion criteria
Age less than 35 and more than 45yrs.
Subjects with previous systemic or ocular pathology.
IOP less than 12 and more than 21 mm of Hg.
Patients who did not give informed consent prior to the study.
Subjects with history of ischemic heart disease.
Subjects with diabetes on insulin medication.
Subjects with history of depression.
Subjects with peripheral vascular disease.
Safety parameters of Timolol In our study. Before giving the eye drop 0.5% Timolol maleate, the history regarding the following were taken. 1. Asthma 2. History of bradycardia 3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 4. Heart block 5. Allergic reaction (example - anaphylaxis, atopy) 6. Blood vessel disease 7. Myasthenia gravis 8. Lung disease 9. Diabetes 10. Glaucoma 11. Stage IV heart failure
After getting approval from the Institutional ethics committee, and informed consent, we recruited 40 emmetropic subjects (80 eyes) between 35-45 years age, and randomly assigned them to binocular once only instillation of one drop of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop (intervention group, 20 subjects) or Normal saline eye drop (Control group, 20 subjects). For every subject, Distant Visual Acuity, Intraocular pressure, Near Point of Accommodation measured by Royal Air Force Rule, were assessed prior to giving eye drop and then at 1/2 hr, 1 hr , 1 ½ hrs , 2 hrs , 2 ½ hrs , 3 hrs, 3 ½ hrs ,4 hrs , 4 ½ hrs, 5 hrs , 5 ½ hrs ,6 hrs and if the effect does not wean off after 6 hrs half hourly examination to be continued till effect started to wean off. We found effect started to wean off after 8 hrs. In control group (Normal Saline eye drop) same measurements were taken. Amplitude of Accommodation was calculated for each NPA value by applying formula as below and included in the data analysis. Formula: A = P-R.
A = Amplitude of Accommodation; P = Refractive power (Dioptre) of eye at NPA=100/NPA;
R= Refractive power (Dioptre) of eye when looking at distance (∞)* = 100/∞=0
*As study subjects are emmetropic.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were expressed as Mean, Median and Standard Deviation and compared across the groups by Mann-Whitney U test since the data did not follow normal distribution as checked using Shapiro Wilk Test. The statistical software SPSS version 25 was used for the analysis. An alpha level of 5% has been taken, i.e. if any p value is less than 0.05 it has been considered as significant.
Results
The intervention and control groups were age and sex matched. The minimum and maximum age in intervention group were 35 years 42 years respectively, and in control group 36 years 44 years respectively. The mean age in intervention and control group were 37.3+/-2.31 years and 38.45 +/- 2.11 years respectively (P = 0.1085). Gender distribution in intervention group was Male: Female = 11(55%): 9(45%) and in control group 15 (75%): 5(25%) (P= 0.185). Hour-wise change of Near Point of Accommodation (in centimetre) and Amplitude of Accommodation (in Dioptre) in the Intervention and Control groups are shown in the Table 1, Table 2 respectively.
Table 1
Hour-wise change of Near Point of Accommodation (in centimetre)
Graphical representations of hour-wise changes of Near Point of Accommodation are depicted; individual tracings of intervention group in Figure 1, that of control group in Figure 2 and comparison between intervention and control groups in Figure 3.
Figure 1
Graph showing individual tracings of NPA of twenty subjects in the intervention group: steady downward slope of NPA tracings soon after instillation of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop till four hours, followed by straightening between four to eight hours.
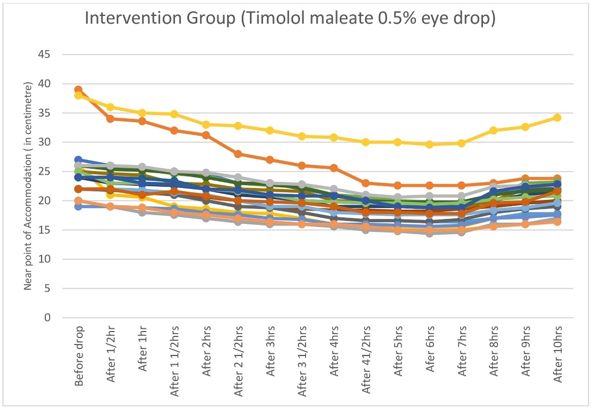
Figure 3
Graph showing comparison of Near Point of Accommodation between Intervention (Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop) and Control group (Normal saline eye drop).
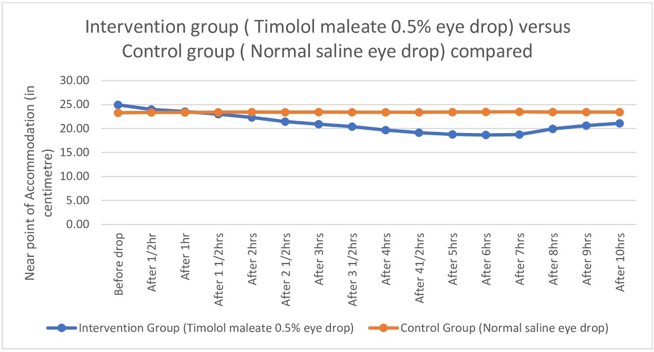
Table 2
Hour-wise change of Amplitude of Accommodation (in Dioptre)
Similarly, graphical representations of hour-wise changes of Amplitude of Accommodation are also depicted in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6.
Figure 4
Graph showing steady upward slope of amplitude of accommodation soon after instillation of timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop till four hours, followed by flattening between four and eight hours.
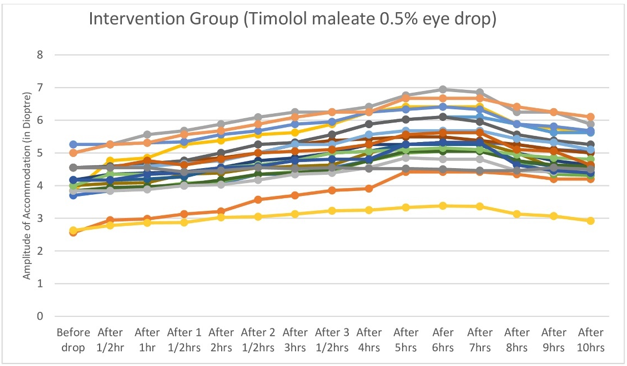
Figure 5
Graph showing normal saline eye drop (Placebo) had no effect on amplitude of accommodation.
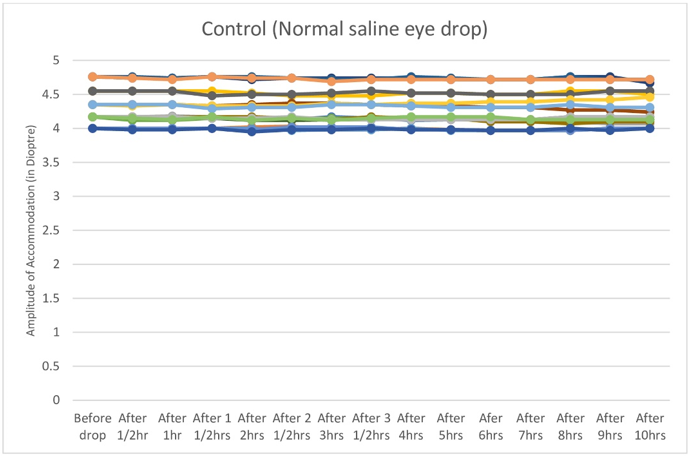
Figure 6
Graph showing comparison of Amplitude of accommodation between Intervention (Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop) and Control group (Normal saline eye drop)
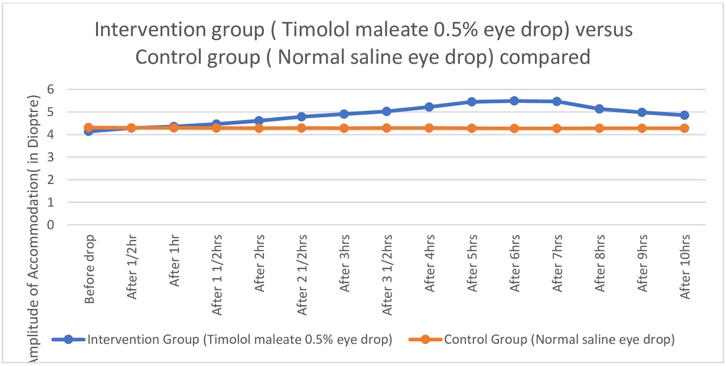
Near point of Accommodation started to come closer and closer to eye steadily and statistically significantly two hours after instillation of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop till four hours after drop, then remained almost stationary between four and eight hours, then the effect started to wean off.(Table 1,Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3) Therefore Near point of Accommodation maintained a steady state between 4 and 8 hrs of instillation, at points closer to eye by an average 5.79 +/- 2.87cm (P < 0.001).(Table 1) This tantamounts to increase of amplitude of accommodation and thus to, presbyopia correction of + 1.21 +/- 0.42 Dioptre (P < 0.001) sustained for 4 hrs between 4hrs and 8 hrs after instillation of drop.(Table 2,Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 )
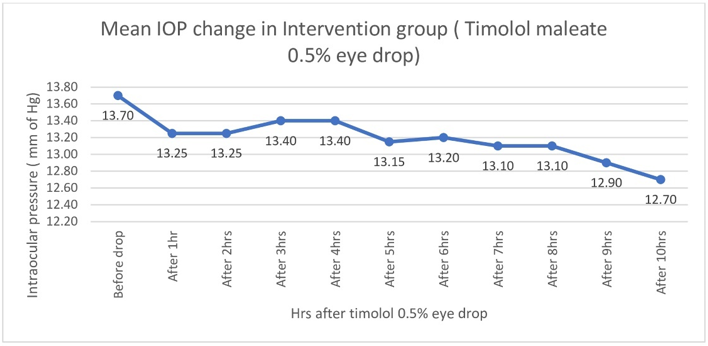
There was no statistically significant fall of intraocular pressure (Table 3, Figure 7) or reduction of distant VA (Figure 8). In the intervention group intraocular pressure never fell below 12 mm of Hg, Distant VA never fell below 6/6 (i.e. pre-drop value)
Table 3
Hourly change of intraocular pressure in Intervention group (Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop) and Control group (Normal saline eye drop)
Discussion
In November 2021, U.S. FDA has approved 1.25% Pilocarpine hydrochloride eye drop for treating presbyopia. This is the only U.S. FDA approved eye drop for presbyopia till date. 20 Pilocarpine causes constriction of pupil and thus causes miosis related side effects like constriction of visual field etc. Roy P et al was first to exploit capsule slackening effect of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop by the mechanism of increased tonic accommodation in hypermature intumescent cataract surgery. 23 Correction of presbyopia as done in our study by this mechanism of action of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop, has not been explored and evaluated before. This mechanism spares pupillary muscles thus does not have any effect on pupillary diameter and also avoids side- effects of multi- drug combination drops which are currently under investigation. The advancing Near Point of Accommodation towards eye and corresponding increase of Amplitude of Accommodation were on expected line as hypothesised. Moreover relieved of relaxing effect on it, excursion of ciliary muscle is now more, covering entire range of accommodation requiring for distant and near vision, thus bringing entire accommodation under facultative control of the individual. Therefore another benefit of exploiting this mechanism lies in that there is no blurring of distant vision as was hypothesized in the beginning of the study. Also as hypothesized there was no statistically significant fall of intraocular pressure.
Conclusion
Binocular once only instillation of one drop of Timolol maleate 0.5% eye drop showed promise for use in the treatment of presbyopia in 35-45 years age group, by adding + 1.2 Dioptre power to refractive system of eye. There was no blurring of distant vision and no significant fall of intraocular pressure. Findings of this research may be utilised for short term near work involving household work like cooking, stitching and office work like lectures, seminars, meetings etc. Future research lies on increasing the duration of action exceeding 4 hrs by instillation of top-up drop.